HTML5 Notes
In this note main content were recorded when we were learning from w3schools HTML5 tutorials. Please go to there to get full and more information.
HTML: Hyper Text Markup Language
HTML version: 1991 start the HTML, until 1999 HTML 4.01, XHTML 1.0 in 2000, then HTML5 in 2012, XHTML5 in 2013.
The <!DOCTYPE> Declaration:
HTML5 only there is one:
HTML4.01:
XHTML 1.0:
HTML5 - New Features
Some of the most interesting new features in HTML5:
_The <canvas> element for 2D drawing
The <video> and <audio> elements for media playback
Support for local storage
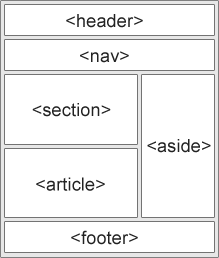
New content-specific elements, like <article>, <footer>, <header>, <nav>, <section>
New form controls, like calendar, date, time, email, url, search_
HTML5 sample code:
- Draw a circle:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3;">
Your browser does not support the HTML5 canvas tag.</canvas>
<script>
var c=document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var ctx=c.getContext("2d");
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(95,50,40,0,2*Math.PI);
ctx.stroke();
</script>
</body>
</html>
- Draw an image:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Image to use:</p>
<img id="scream" src="img_the_scream.jpg" alt="The Scream" width="220" height="277"><p>Canvas:</p>
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="250" height="300" style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3;">
Your browser does not support the HTML5 canvas tag.</canvas>
<script>
var c=document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var ctx=c.getContext("2d");
var img=document.getElementById("scream");
ctx.drawImage(img,10,10);
</script>
</body>
</html>
HTML5 has support for inline SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
Canvas vs SVG:
SVG is a language for describing 2D graphics in XML.
Canvas draws 2D graphics, on the fly (with a JavaScript).
Canvas is rendered pixel by pixel.
Canvas:
Resolution dependent
No support for event handlers
Poor text rendering capabilities
You can save the resulting image as .png or .jpg
Well suited for graphic-intensive games
SVG:
Resolution independent
Support for event handlers
Best suited for applications with large rendering areas (Google Maps)
Slow rendering if complex (anything that uses the DOM a lot will be slow)
Not suited for game applications
SVG sample:
- Draw a file angles star
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body><svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1" height="190">
<polygon points="100,10 40,180 190,60 10,60 160,180"
style="fill:lime;stroke:purple;stroke-width:5;fill-rule:evenodd;">
</svg>
</body>
</html>
HTML5 events:
Mouse drag and drop sample (about full content and detail explanation, please read w3schools web page ):
…
<script>
function allowDrop(ev)
{
ev.preventDefault();
}
function drag(ev)
{
ev.dataTransfer.setData("Text",ev.target.id);
}
function drop(ev)
{
ev.preventDefault();
var data=ev.dataTransfer.getData("Text");
ev.target.appendChild(document.getElementById(data));
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1" ondrop="drop(event)"
ondragover="allowDrop(event)"></div>
<img id="drag1" src="img_logo.gif" draggable="true"
ondragstart="drag(event)" width="336" height="69">
Get User’s Geo location:
<script>
var x=document.getElementById("demo");
function getLocation()
{
if (navigator.geolocation)
{
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(showPosition);
}
else{x.innerHTML="Geolocation is not supported by this browser.";}
}
function showPosition(position)
{
x.innerHTML="Latitude: " + position.coords.latitude +
"<br>Longitude: " + position.coords.longitude;
}
</script>
HTML5 Video:
<video width="320" height="240" controls>
<source src="movie.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="movie.ogg" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
< /video>
HTML5 New Semantic Elements:
(the image is on w3schools)
HTML5 Web Storage:
The old way for web page data storage was done with cookies.
Web Storage is more secure and faster.
The data is used ONLY when asked for;
Be able to store large amounts of data, without affecting the website's performance;
The data is stored in key/value pairs, and a web page can only access data stored by itself.
HTML5 Web Worker:
A web worker is a JavaScript running in the background, without affecting the performance of the page.
HTML5 Server-Sent Events:
A server-sent event is when a web page automatically gets updates from a server.
This feature looks like the server push data to clients.